The GL serves as the basis for a company’s income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. By keeping your general ledger up-to-date, stakeholders, investors and analysts can accurately assess the company’s performance. You may choose to conduct an internal audit or get your accounts audited by an accounting professional, so your general ledger acts as an important financial record.
- The report can print incomestatement, balance sheet, or all balances for a selected range ofaccounting combinations.
- Having proper ledger accounts help you to prepare a trial balance sheet, meaning you can verify the accuracy of your accounts and prepare final accounts.
- Additionally, if you make errors in updating or recording transactions, the GL account balances will be incorrect.
- A subledger is a detailed record of transactions related to a particular financial account, like inventory or payroll.
Format of a Self-balancing Ledger Account
Debiting an asset or expense account increases its current balance, while crediting them decreases it. Conversely, crediting a revenue, liability, or equity account increases its current balance, and debiting them increases it. The general ledger is a foundational accounting document that contains a record of all your business’ activities. For each entry in your chart of accounts, it displays a sub-ledger documenting the details of every transaction affecting it, culminating in the account’s running balance. The best way to know if your general ledger is correct is to reconcile all entries then generate a trial balance to verify the completeness and ensure that debit balances equal credit balances. Having an accurate record of all transactions that have taken place within a single point in time will ensure your financial reporting is done correctly.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
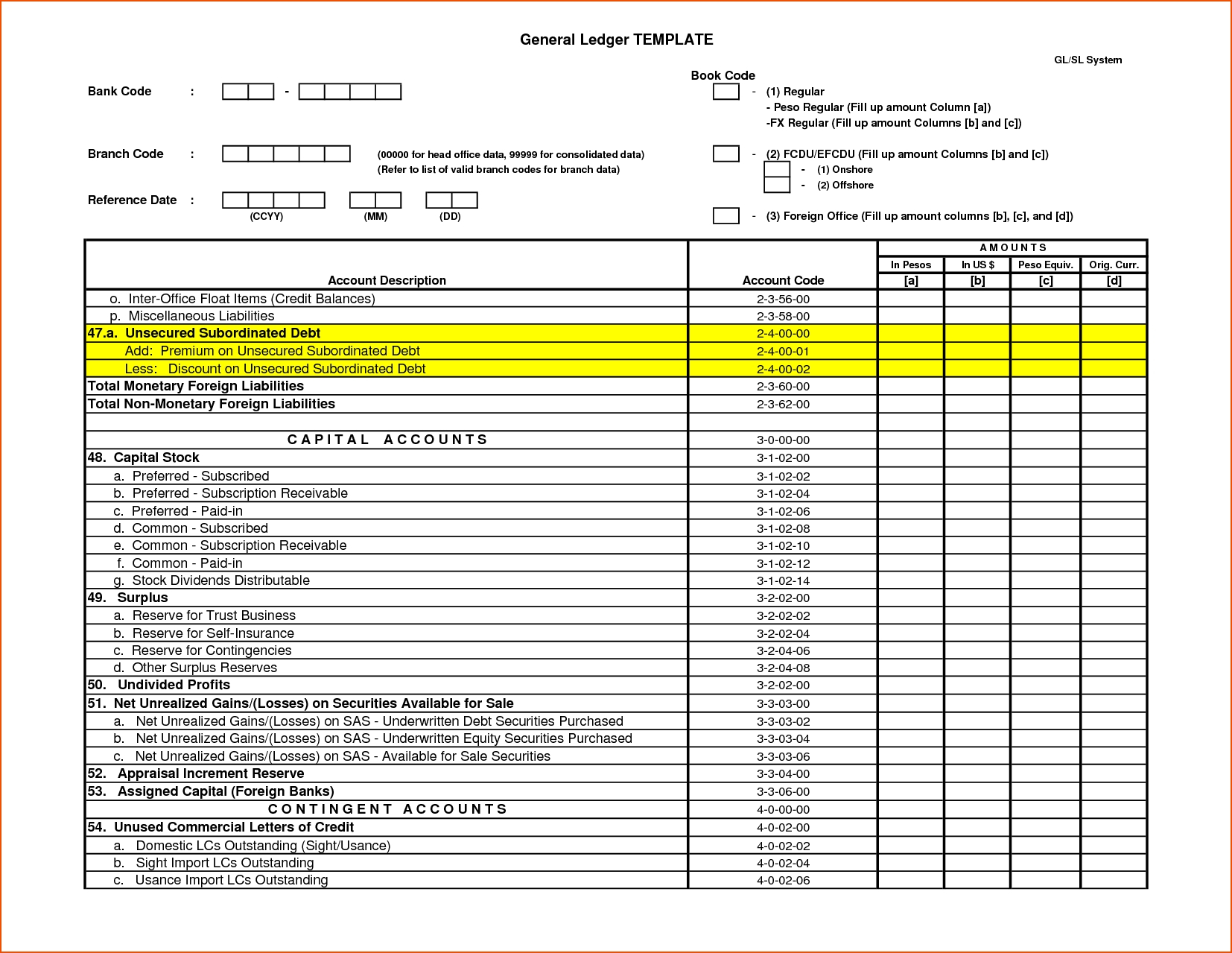
Accounts are usually listed in the general ledger with their account numbers and transaction information. Here is what an general ledger template looks like in debit and credit format. Are you a small business owner looking to understand general ledger accounting? In this guide, we’ll provide you with an introduction to where general ledgers fit into small business accounting. Since every transaction affects at least two accounts, fully recording its impact on the ledger requires us to make two entries for each transaction. This is to ensure that each transaction affects the balance sheet in such a way that an increase on one side of the balance is offset either by a decrease on the same side or by an increase on the other side.
Step #2: Post journal entries
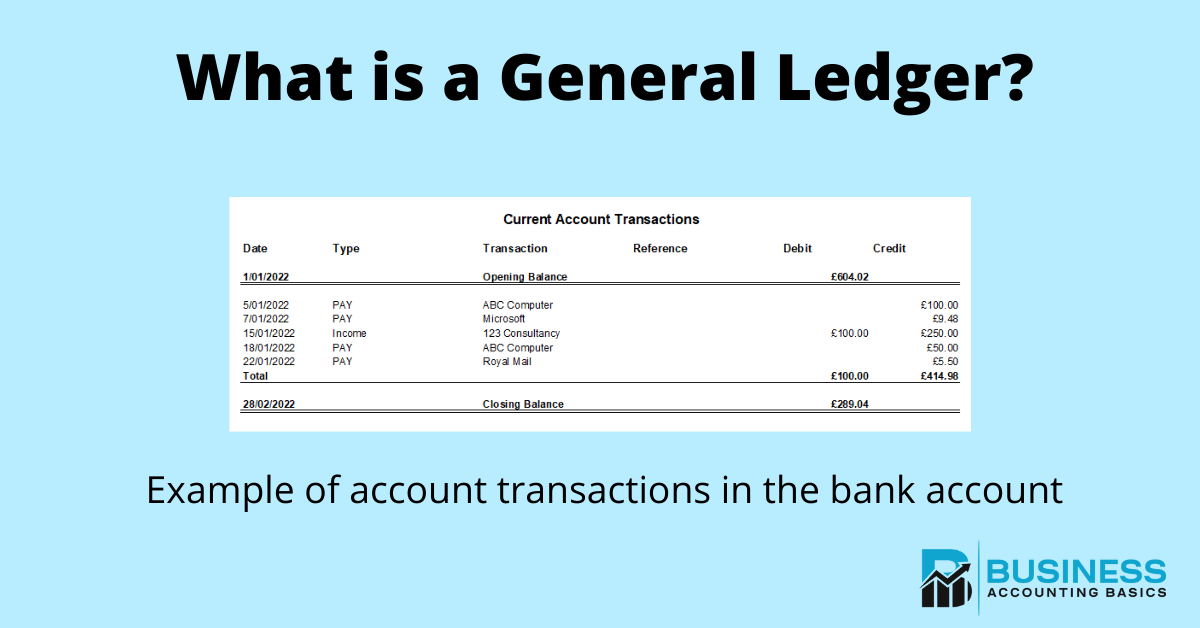
Now that you’ve learned more about what a general ledger is in accounting, you’ll be better able to provide your accountant with the information they need to keep your books balanced. In double-entry bookkeeping, each transaction will affect at least 2 accounts. For example, you’ll need to record rent expenses every month if you rent computers and decide to prepay the rent in January for the next twelve months.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
As a result, you do not record details of each sales transaction undertaken with your customers in the accounts receivable control account. But, you can refer to the related subsidiary account if you need to check any detail regarding the sales made to a specific customer. A control account operates the same as general ledger account but you record only the summarized information regarding a specific account. It does not contain detailed information related to such an account, so you need to refer to a related subsidiary ledger in order to get details of such a control account. A sales ledger, or debtors ledger, is one of the three types of ledgers that you prepare as a firm or a business entity. It records all the transactions that take place between you and your debtors.
A general ledger has four primary components, these include a journal entry, a description, debit and credit columns, and a balance. Consider the following example where a company receives a $1,000 payment from a client for its services. The accountant would then increase the asset column by $1,000 and subtract $1,000 from accounts receivable.
In accounting, a general ledger is used to record a company’s ongoing transactions. Within a general ledger, transactional data is organized into assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and owner’s equity. After each sub-ledger has been closed when is the end of this quarter out, the accountant prepares the trial balance. This data from the trial balance is then used to create the company’s financial statements, such as its balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and other financial reports.
Here is an example of how you can transfer the journal entries to a general ledger. The general ledger contains a chart of accounts, which is a list of all accounts that can be found within the ledger that are used by the business. Accounts payable is the money a company owes to its suppliers and vendors for products and services purchased on credit.
The general ledger is a foundational document in the double-entry accounting system, the most widely accepted modern accounting method. It requires that all financial transactions affect at least two accounts and balance between debits and credits. However, reconciling individual account balances becomes extremely easy with online accounting software like QuickBooks. This feature automatically matches the transactions recorded in your books of accounts with the bank statement balances. A general ledger contains information related to different accounts, providing information that helps you in preparing your business’ financial statements, including income statements and balance sheets.
Each type helps categorize and organize financial data for reporting and analysis. This is where your accountant makes the original entry for your financial transactions and dates them. All transaction data comes to the general journal and makes its way to the general ledger. Sub-ledgers are particularly helpful for businesses with a high sales volume because you can segment your financial transactions into digestible categories, making managing your financial data easier. Journal entries are the records accountants use to document transactions and update their account balances.

Leave a Reply